Particles hitting the wire can interact or undergo quasi elastic scattering. At high energies (;SPMgt; 10 Gev) the cross sections depends only weak on the energy. The total cross section of protons impinging on a nuclei with atomic number A ;SPMgt; 4 is given by:
![]()
![]() is on the other hand given by the sum of the
elastic and inelastic
crossection (
is on the other hand given by the sum of the
elastic and inelastic
crossection ( ![]() )
with:
)
with:
![]()
The ratio ![]() can be parametrised within a few percent
accuracy by:
can be parametrised within a few percent
accuracy by:
![]()
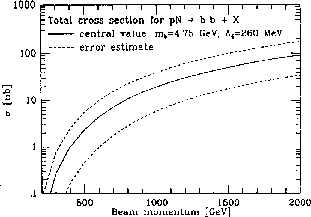
Figure 5: QCD calculations up to ![]() for
for ![]() .
.
The HERA proton beam energy of 820 GeV leads in a fixed target environment
to a center of mass energy ![]() ,
an energy not to fare above the b threshold.
The background of normal inelastic interactions dominates b production
by six orders of magnitudes. At HERA energies the gluon fusion processes,
,
an energy not to fare above the b threshold.
The background of normal inelastic interactions dominates b production
by six orders of magnitudes. At HERA energies the gluon fusion processes,
![]() , provides about 85% of the heavy quarks, the rest
is produced by quark annihilation,
, provides about 85% of the heavy quarks, the rest
is produced by quark annihilation, ![]() .
Fig. 5 shows the results of QCD calculations
up to
.
Fig. 5 shows the results of QCD calculations
up to ![]() [8].
They predict a
[8].
They predict a ![]() cross section of about 12 nb at
820 GeV beam energy, but with large uncertainties.
The predicted value is in reasonable agreement with
various measurements which also incorporates large uncertainties.
This picture also clearly indicates that an increase in the HERA
proton energy, which is now under serious investigation
cross section of about 12 nb at
820 GeV beam energy, but with large uncertainties.
The predicted value is in reasonable agreement with
various measurements which also incorporates large uncertainties.
This picture also clearly indicates that an increase in the HERA
proton energy, which is now under serious investigation![]() would increase the b-yield and
therefore the signal to background ratio significantly.
The
would increase the b-yield and
therefore the signal to background ratio significantly.
The ![]() cross section increases nearly linear with A:
cross section increases nearly linear with A:
![]()
Therefore the
fraction of events with heavy quarks increases slowly with A.
On the other side the mean number of tracks per interactions
increases roughly like ![]() .
For the experiment, mainly limited by the occupancy in the detector,
one achieves a slight gain in the number of produced b quarks per
interaction to the
number of tracks per interaction in the range of 20-30% for heavy targets
compared to light targets.
There are more b's per interaction
for heavy materials. Therefore one also gain in the number of
vertices per bx - a number which is preferably small.
But for the target material choice
one has to take into account various other
points like target efficiency, target induced background
and momenta distribution of the tracks which usually prefers light materials.
.
For the experiment, mainly limited by the occupancy in the detector,
one achieves a slight gain in the number of produced b quarks per
interaction to the
number of tracks per interaction in the range of 20-30% for heavy targets
compared to light targets.
There are more b's per interaction
for heavy materials. Therefore one also gain in the number of
vertices per bx - a number which is preferably small.
But for the target material choice
one has to take into account various other
points like target efficiency, target induced background
and momenta distribution of the tracks which usually prefers light materials.