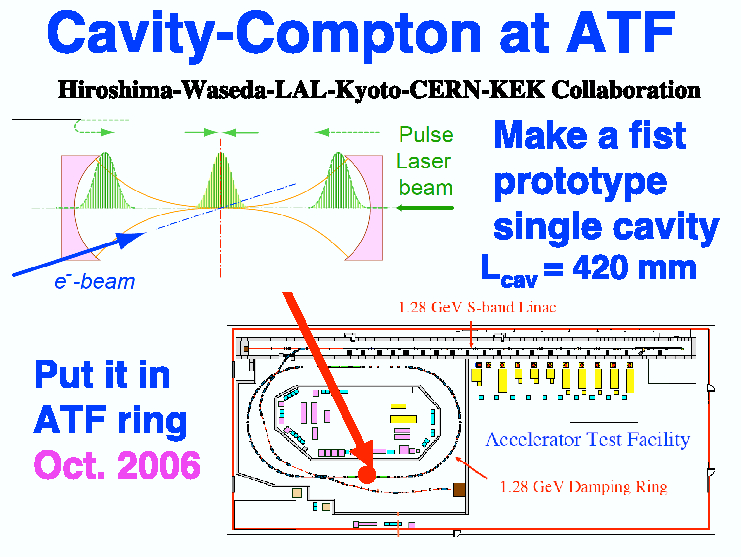
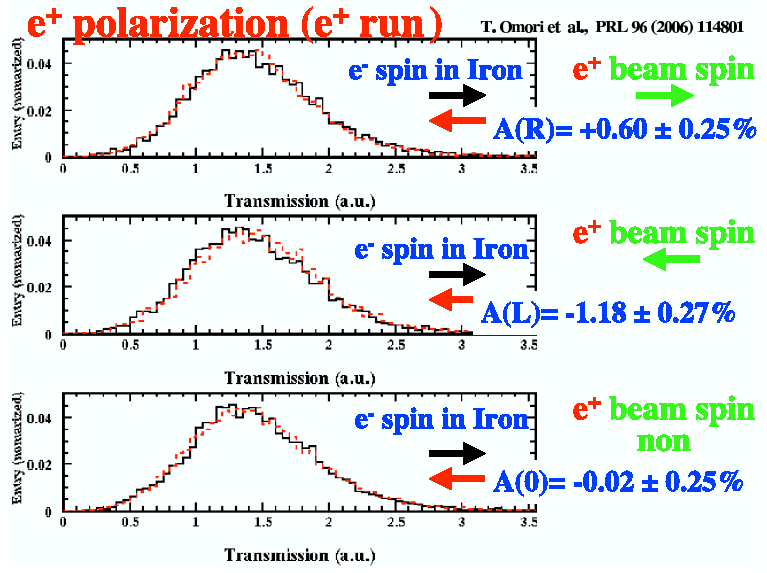
 Both
photon and
positron
asymmetries have been measured via transmission
polarimetry, see explained in the box above.
Both
photon and
positron
asymmetries have been measured via transmission
polarimetry, see explained in the box above.
The measurements were done for left- and righ-polarized laser light. Changing the laser polarization
flips the positron polarization. Furthermore the asymmetry was also measured for linear laser polarization, which should
correspond to zero longitudinal polarization of the positrons.
All measurements
were perfectly consistent with the theoretical expectations.
|
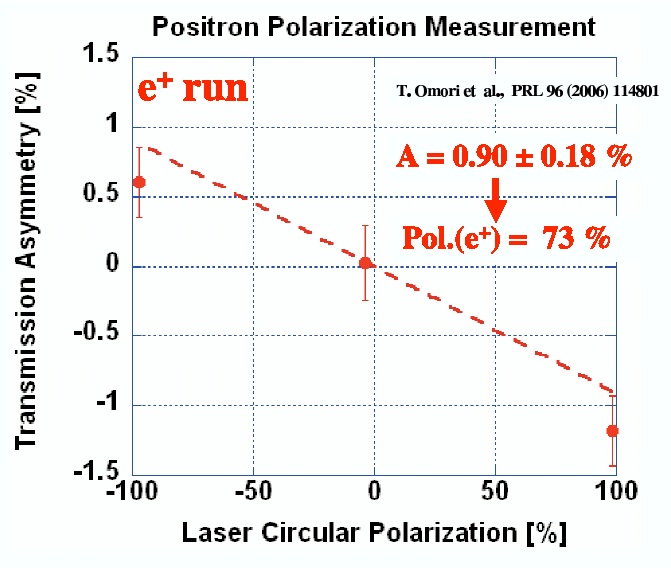 In order to derive the polarization from the measured asymmetries a
straight line was fitted to the data,
constrained by passing through the origin. The absolute value of the slope obtained to be 0.90 +- 0.18%.
The slope corresponds to the positron asymmetry assuming
100% laser polarization.
In order to derive the polarization from the measured asymmetries a
straight line was fitted to the data,
constrained by passing through the origin. The absolute value of the slope obtained to be 0.90 +- 0.18%.
The slope corresponds to the positron asymmetry assuming
100% laser polarization.
From this asymmetry, the magnitude of positron polarization was calculated to be 73% +- 15% (stat. error) +- 19%
(syst. error due to Monte-Carlo simulation).
The measurement was also done for electron polarization. All results, those for positron polarization and
those for electron polarization, are in agreement with each other.
|
|
The incoming 10^10 electrons per bunch were leading to about 10^7 photons per bunch.
The conversion into positrons at the
1mm-thick W target is about 9%
in that photon energy range of ~56 MeV. Only high-energy positrons of about 10^4 positrons per bunch
were extracted.
The momentum of the positrons was not measured, but the average energy of the positrons is, according
to the simulation, at about 36 MeV with a r.m.s. width of 8 MeV.
More details about the ATF-Compton experiment
are given in Phys.Rev.Lett. 96, 114801 (2006).
|
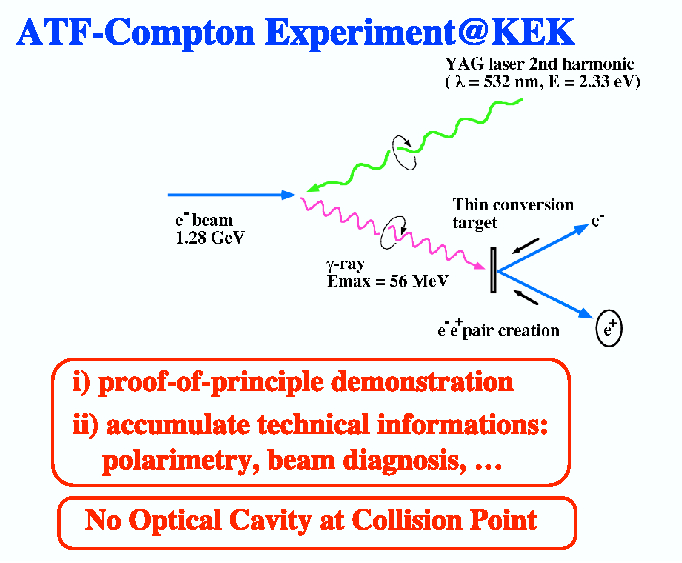 The ATF-Compton experiment at KEK
presents the `proof-of-principle-experiment'
for the laser-Compton based scheme to produce polarized positrons.
The ATF-Compton experiment at KEK
presents the `proof-of-principle-experiment'
for the laser-Compton based scheme to produce polarized positrons.